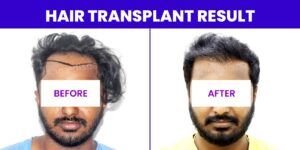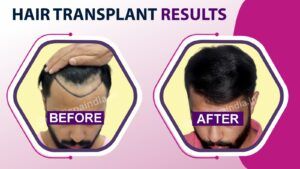
Advertising portrayals of the hair transplant surgery as being very straightforward are only partially accurate because the treatment takes extensive planning before being carried out. Extensive knowledge, skilled hands, an eye for beauty, and a wealth of experience are undoubtedly required for good results. Customers trust less expensive clinics because of false claims that hair transplant procedures are risk-free, but many later regret it when the results are mediocre. By going with a less expensive hair transplant clinic, you run the risk of losing your life and getting subpar results.
In order for the hair grafts to survive, the tiny, incredibly delicate hair follicles that are harvested during the hair transplant procedure must be treated delicately during extraction and implantation by trained hands. If the hair follicular grafts survive, only you can get the maximum hair density possible. The success of the treatment depends on the surgeon’s competence and experience, so you must choose the hair transplant surgeon carefully.
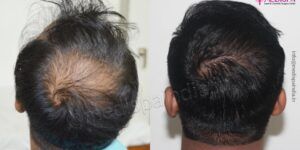
The fantastic hair transplant in Delhi has become a widely recognised treatment for the problem of hair loss and is welcomed by people from all over the world who go to the city to receive the treatment. Due to their superior services, highly experienced surgeons, and great skilful hands which have excelled them in the field of hair transplant, a select few of the city’s hair transplant clinics have won the trust of the international patient.
One of the most well-known hair transplant surgeons in the nation, Dr. Suneet Soni practises in Delhi and Jaipur and is the head and director of the Medispa hair transplant clinic. He is aware of the fact that adopting new developments in this area is crucial, and that striving for perfection in the management of these microscopic hair transplants includes looking out refinement and ways to get better.
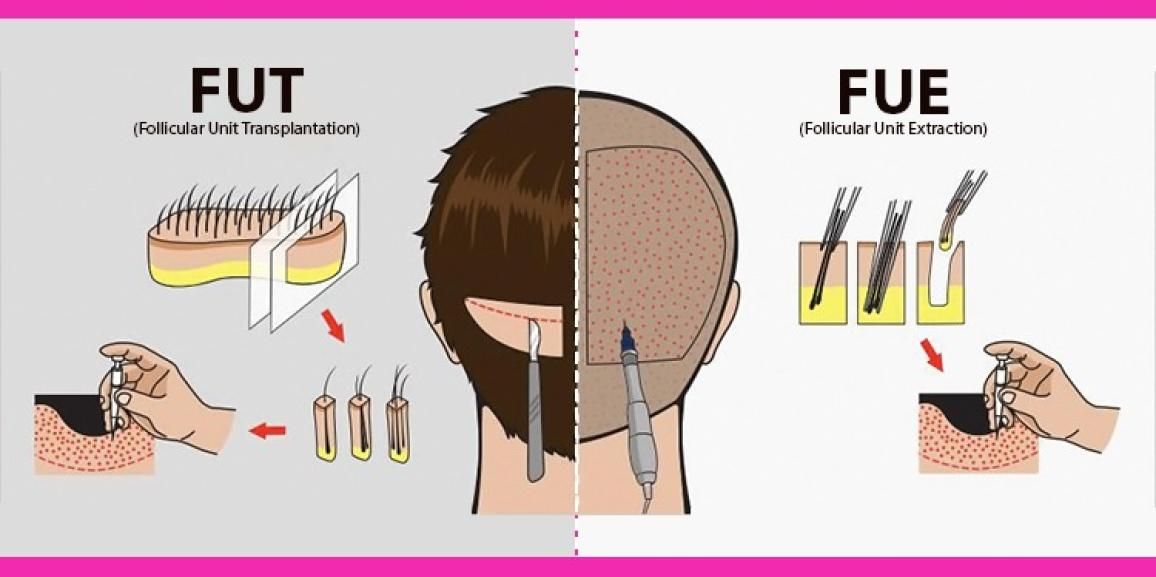
Ways to harvest the hair grafts for hair transplantation
The two main techniques for carrying out the procedure-FUT and FUE hair transplant-are defined by how the hair transplants are harvested. Following is an explanation of this:
- FUT or strip hair transplantation: In a FUT hair transplant, the donor area of the scalp is excised into a thin strip, which is then separated to harvest individual hair grafts. These individual hair transplants are carefully placed in the ideal bald area while creating the hairline. Trichophytic closure is a cutting-edge method for restraining the donor region. With this approach, around 3000–3500 hair grafts can be harvested, which is sufficient for covering significant baldness or producing high density hair transplant.
- FUE hair transplant: This treatment involves pulling the hair grafts from beneath the scalp skin using a motorised or manual punch device. The recipient’s bald area is then directly covered with these individual hair grafts. Each hair graft is removed from a larger interspace, minimising scarring at the donor location after the wound has healed.
Why hair graft damage in FUT is less than the FUE technique?
Let’s examine why FUE hair transplantation has a higher rate of damage than FUT:
- Better visibility when dividing the hair grafts: When doing FUT hair transplant, the hairs are extracted from an excised strip under higher magnification, which lowers the damage rate to hair grafts. On the other hand, the hair grafts removed using the FUE technique are pulled blindly while assuming the location of the roots beneath the tissues, making the grafts more vulnerable to harm.
- Hair grafts are not tugged during harvesting; as a result, they are not as delicate as hair grafts removed using the FUE procedure and are less likely to be damaged.
- Better standing of hair grafts at longer out-of-body times: The FUT procedure involves separating the excised strip to harvest the hair grafts, which keeps the grafts safe and permits longer out-of-body times of more than 8 hours. On the other hand, the FUE procedure involves pulling pressures that render the hair grafts fragile and susceptible to harm the longer they remain outside of the body.