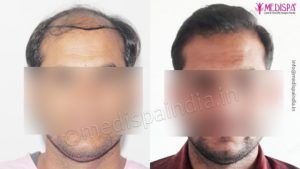
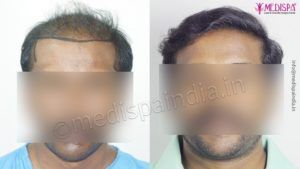
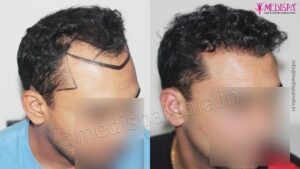
A hair restoration procedure is a kind of popular surgical treatment that aims at enhancing the looks of a person by implanting the hairs at the site of baldness. In the modern societies, the hair transplant treatments have gained a tremendous popularity as the number of people affected by the problem of hair loss has witnessed a significant rise in the past few years.
Even though the FUE treatment has emerged as an alternative method to the conventional strip method or the Follicular Unit Transplant method, it is still less preferred as it cannot promote maximum coverage in the higher grades of baldness. Whereas in a Follicular Unit Transplant, a plastic and cosmetic surgeon may utilize a large number of grafts to promote maximum coverage even to higher grades of baldness. On another hand, the people opting for Follicular Unit Transplant (FUT) often have a doubt about the scar produced due to the harvesting of the strip.
This article is a complete guide on the donor incision and the significance of the trichophytic closure to minimize the appearance of the scar. Continue reading to know more about it.
The position of donor incision–
In a FUT hair transplant, the donor strip is harvested from the safe donor area in the back of the scalp. The safe donor area lies in between the vertex and the neck portion. Generally, the incision is made in the middle of the safe donor zone in the form of a band that starts above the small bump in this zone. The incision extends to either side of the scalp, having a subtle curvature and points upwards.
Size of the donor strip-
On an average, the count of hair follicles available on a person’s head is 65-85 follicular units per cm square. The width of the harvested strip is generally kept around 1-1.5 cm wide and its length is adjudged on the basis of desired number of hair bulbs to impart coverage to the affected area. Some factors that determine the size of the strip are-
- The laxity of the scalp
- Quality of donor area
- Grade of baldness
Closure of the donor incision–
Closing the incision at donor site is perhaps the most important part of the FUT hair transplant procedure. In earlier times, the donor incision was closed by using two-layered closing. But the scar produced in this process was much prominent and was a matter of concern for most of the people. On another hand, the introduction of trichophytic closure method in the field of hair transplant, the scar can now be made to appear as a super-fine line which is almost invisible.
The trichophytic closure-
Trichophytic closure or commonly known as ‘tricho’ involves overlapping the edges of the wound while suturing or stapling them. In this method, an oblique cut is made on one side of the existing skin and thereafter, the adjacent layer of the skin is brought closer and both flaps of the skin are stitched together to close the wound. Due to the angle of the cut, both the layers of the skin overlaps and one piece of scalp tissue lies underneath another layer, hence concealing the scar and making the donor area look natural.
Importance of a trichophytic closure-
In case of a FUT hair transplant, the wound is closed by using the trichophytic closure, which leads to an appearance of the scar as a superfine line. As the hairs grow, the appearance of superfine scar becomes invisible and almost unnoticeable.
The trichophytic closure is highly appreciated by the people who love to wear short hairstyles. It can also be used on patients who have already undergone a FUT to improve the donor scar.