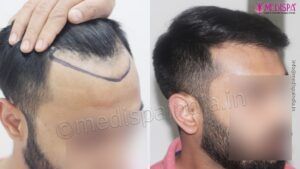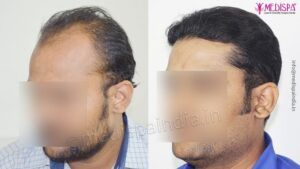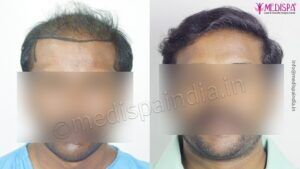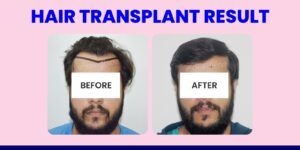
Over the globe, more than 60% of men and 50 % of women suffer from hair loss. The most common hair loss condition is Androgenetic alopecia, which is a semi-natural process depending on the genetics of the individual and can only be temporarily inhibited with medications. The medications available for preventing Androgenetic alopecia include oral Finasteride and topical Minodoxil solution. For females, topical Minodoxil is the most effective treatment for Androgenetic alopecia. However, there are no medications available which can restore the hairs which are already lost. For the permanent solution of hair loss, hair transplant is the only treatment which provides highly promising results.
What is a hair transplant?
Hair transplant is a surgical procedure in which hairs from one donor site are extracted and transplanted to area of baldness or hair loss, where they continue to grow. The procedure of hair transplantation was introduced in 1950s by Dr. Orentreich. He started with using 4 mm punches for extraction of hair follicles. Over the years there have been a lot advancements in the hair transplant procedures. At present, most commonly used techniques for hair transplantation are Follicular Unit Hair Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE).
Follicular Unit Hair Transplantation (FUT)
FUT is a most frequently used hair transplant technique introduced in later 1990s. In this method, harvesting of hair follicles from donor area is done by excising a single skin strip from the donor area followed by suturing. The disadvantage of this method is the residual scar at the donor site after the procedure. However, by employing newer trichophytic closure technique, it is possible to provide a fine linear scar. However, there are few patients who choose to wear short hairs and FUT procedure would be inappreciable in them.
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
FUE procedure, also known as FUSE (Follicular Unit Separation Extraction) method, Wood’s technique, FU Isolation method, is gaining popularity swiftly as an alternative to FUT in certain cases. In this technique of hair transplantation, the hair grafts are individually extracted from the donor site using a micro motor. Although, there are numerous drawbacks to this method, various researches and advancements are taking place to overcome the limitations of extraction of grafts from donor area.
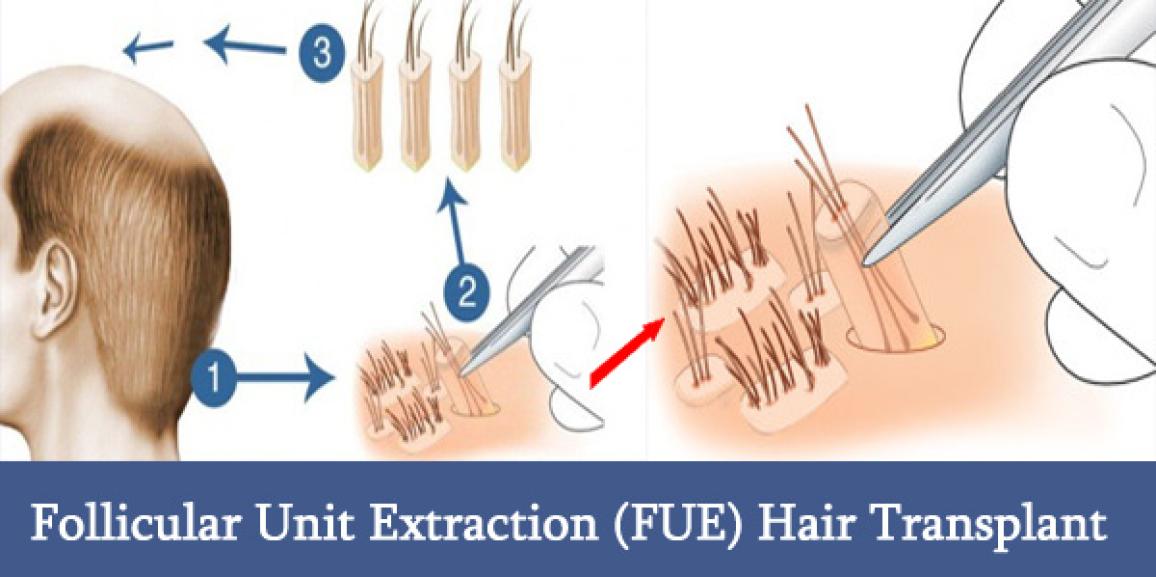
Procedure of FUE:
The procedure of follicular unit extraction is different from the procedure of FUT or follicular unit transplantation. This technique is a suture less method of hair restoration which consists of extraction of hair follicles from the donor areas and implanting the same in recipient areas. The detailed procedure of FUE is given below.
On the day of surgery, firstly the donor area of the patient is trimmed short to 1-2 mm of hair length. Then, patient is prepared for the surgery and seated on the operating table in a position that allows easy access to the head to the doctor. Then, local anaesthesia is administered at the donor site to numb the operating area. After the effect of anaesthesia is achieved, a special type of micropunches is used for extraction of hair follicles from the donor scalp area. While performing extraction of the hair follicles, the doctor uses magnification to see the follicles clearly.
The extracted hair follicles are stored in normal saline during the procedure to keep their viability intact. The duration of harvesting process depends on the number of hair grafts required for extraction. After the completion of extraction procedure, implantation phase for hair grafts is started. In this phase, a slit is created by the surgeon at the recipient site. The hair graft is then placed in the slit.
Requirements for performing follicular unit extraction:
- The person who is performing the surgery should be a board certified plastic and cosmetic surgeon.
- High experience and training of the surgeon.
- Excellent lighting in the operation theatre.
- Sufficient magnification for the surgeon and accompanying staff.
- The surgeon should perform the procedure with proper hand motion. While doing the twisting motion of the punch, the hand should be perfectly stable. Also, clockwise rotation of the punch provides more stability than twisting the punch in anti-clockwise direction.
- Surgeon should be able to judge and determine the angle of root of hair below the surface of skin because the angle of hair root is generally more acute than the angle of hair above the skin.
- The punch size should be kept in the range of 0.6-1 mm as this size of the punch is suitable large for extraction of follicles, and as well minimise the size of wound and thus minimise the scarring.
- The choice of sharp punches or blunt punches should be done appropriately. Few surgeons prefer using sharp punches for two-step technique so as to minimise the amount of twisting needed for cutting into the dermis. On the other hand, to decrease the follicular transection rate, blunt punches are used in 3 step technique.
Indications for FUE:
- Patients who do not want a linear scar at the back of head or want to wear hair very short
- Patients who themselves request FUE procedure and have enough donor supply to be harvested to meet their needs.
- For patients who require small sessions for less severe hair loss such as patients with Norwood grade 3 hair loss or cosmetic areas such as widow’s peak, eyebrows, eyelashes, etc.
- For camouflaging residual scars from previous FUT procedure.
- For covering scars from trauma, neurosurgical procedures or dermatological conditions.
- When subsequent sessions for strip procedure are not possible, then FUE is indicated for extraction of hair follicles.
- For sports individuals, who require restarting their training immediately after the procedure.
- For cases where donor area is body hairs or beard.
Contraindications for FUE:
- Inadequate experience of surgeon in performing FUE techniques.
- Proper instruments not available at the centre.
- Patients expectations which cannot be fulfilled.
- Donor supply restricted.
- Severe grade baldness such as grade 6 or 7. In such cases, because of limited donor supply, only FUE cannot be done.
- For patients who are uncooperative to undergo the procedure for long sessions or for multiple sessions because of the slowness of the procedure.
- Patients who do not want to cut short their hairs such as women.
- Bald areas which require more than 2500 grafts for the restoration.
Advantages of FUE over FUT:
Both FUE and FUT are techniques of hair transplantations, however, there are some differences in both the techniques. Firstly, no postoperative visible scar is seen after the FUE procedure. Let’s discuss the advantages of FUE procedure with respect to surgeon and patient’s perspective separately.
Advantages of FUE to surgeon:
- Less manpower required as compared to FUT procedure. One doctor with 1-2 assistants can perform the procedure.
- As compared to FUT, the FUE procedure is less traumatic and does not cause surgical fatigue to the patient after the completion of the surgery.
- Minimal preparation required for hair grafts
- Less equipment required for the procedure as compared to FUT where a team of technicians along with video assisted microscopes are required for dissection of hair grafts.
Advantages of FUE to patient:
- Can wear short hairs
- Less postoperative recovery time period required
- Almost practically invisible microscopic scars in the donor area
- No stiches in the donor area
- Can be utilized along with FUT procedure to utilise the donor area efficiently in case of severe grade baldness
Limitations of FUE procedure:
- FUE is a tiring procedure as it requires extraction of individual hair grafts from the donor area. It effects surgeon’s patience and energy level significantly.
- Higher transection rate: This remains the main area of concern with this technique. The frequent lack of association between the exit angle of the hair and the subcutaneous course of the follicle is particularly problematic. When this is coupled with frequent changes in follicle direction, the follicular transection rate (FTR) is more. In order to maintain the reliability of FUE, it is indispensable to remain within a permissible level of follicle transection rate (FTR), at least comparable to the standard technique of strip harvesting and microscopic dissection, which has a transection rate of approximately 2%.
- Tethering of the follicle to dermal components may require either time-consuming dissection or shearing of the follicles as extraction is attempted.
- The procedure is long and hence tiring for the patient. Patient also has to lie in the prone position which adds to the discomfort.
- Finally, the number of grafts extracted per day is limited, leading to multiple sessions over several days. To overcome this, surgeons have introduced megasessions. Currently, in some clinics, FUE megasessions up to 2000 grafts over 10–12 hours session in a day are performed. One recent study reports extracting up to 4400 grafts over 3 days.
- Some surgeons in order to extract higher number of grafts may risk going into the temporary zone; the hair follicles extracted from this region may be lost forever.
- Very fine trimming of donor hair which is disadvantageous to many people.
Cost of FUE Hair Transplant
Let’s discuss the most important issue for hair transplant, cost of hair transplant procedure. This answer cannot be summarised in a single line because it depends on a number of parameters.
- Hair transplant procedure: The price of hair transplant highly depends on the technique used by the surgeon to perform the transplant. The usual cost of FUE transplant is more as compared to FUT technique.
- Severity of baldness: The area of recipient site which needs implantation of hair grafts highly affects the price of FUE hair transplant. With increased severity of baldness, more number of grafts is required for its restoration. As the cost of FUE hair transplant is decided on the basis of per graft cost, so, more the number of grafts required, more will be the cost of the FUE hair transplant.
- Surgical experience and expertise of the surgeon: The price of the hair transplant also varies on the surgical expertise and experience of the hair transplant surgeon. Experienced plastic and aesthetic surgeons, who are most qualified for handling such a technique sensitive procedure cost generally more than usual doctors.
- The geographic location of the surgeon: The cost of the FUE hair transplant depends highly on the location and country. Ordinarily, the cost of FUE hair transplant in US, UK and Canada is 70-80 % expensive as compared to cost in India, even though the Indian clinics are providing world class treatments and highly optimistic results.